The History of Artificial Intelligence
From its beginnings to the present day.
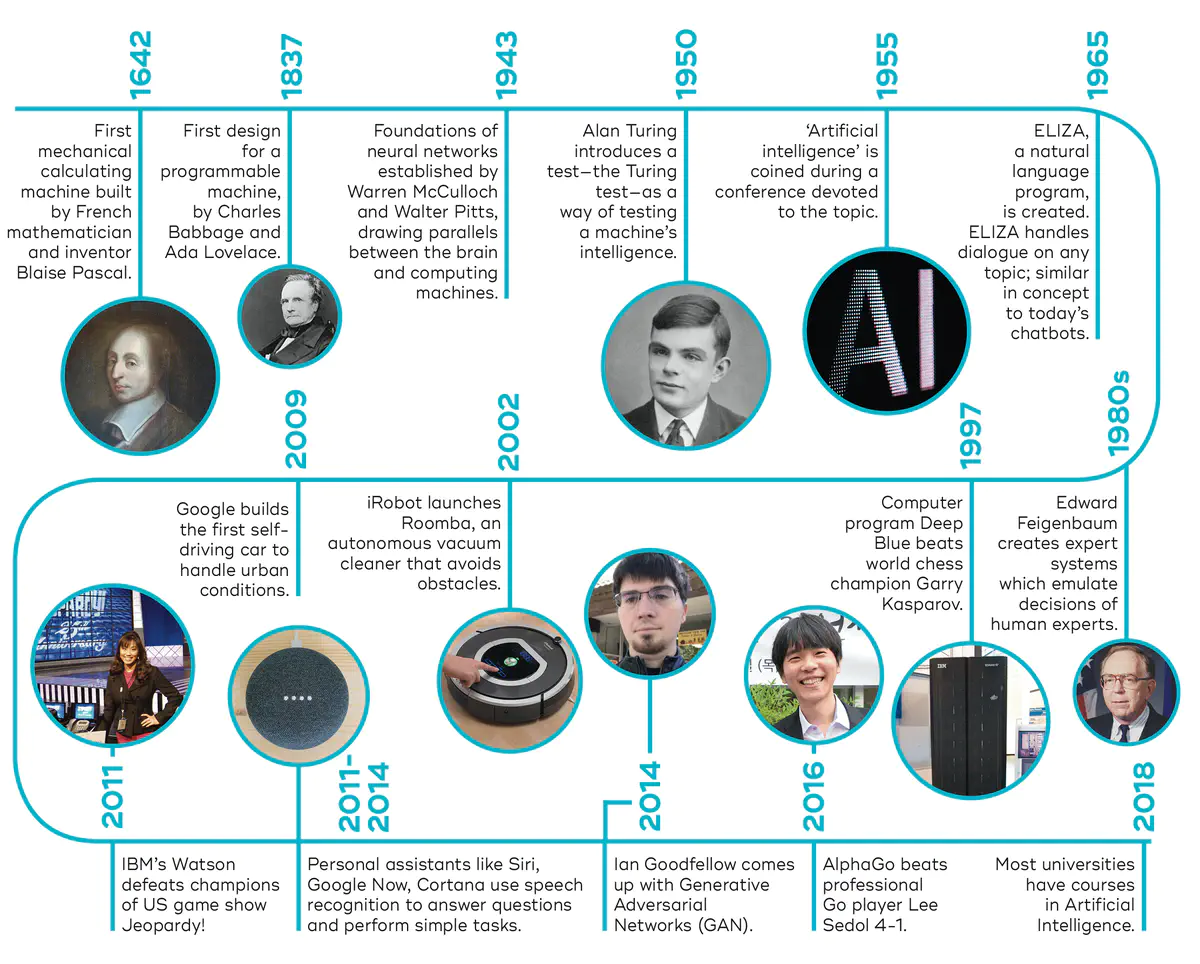 Image credit: qbi
Image credit: qbiOverview
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a rapidly growing field that has the potential to revolutionize many aspects of our lives. From self-driving cars and personal assistants to medical diagnosis and financial forecasting, AI is used in many applications. But where did this technology come from, and how has it evolved over time?
In this blog post, we will take a look at the history of AI, starting with its earliest roots and tracing its development through to the present day. We will highlight some of the key events and milestones in the field, and discuss some of the current trends and future directions for AI.
The Early Years: 1950s-1960s
The origins of AI can be traced back to the 1950s, when researchers first began to explore the possibility of creating intelligent machines. One of the earliest and most influential figures in the field was Alan Turing, a British mathematician and computer scientist who is often referred to as the “father of modern computing.” In 1950, Turing published a paper titled “Computing Machinery and Intelligence,” in which he proposed the “Turing Test” as a way to determine whether a machine could be considered intelligent.
Other early pioneers in the field of AI included researchers such as John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, and Claude Shannon, who founded the first AI laboratory at Dartmouth College in 1956. This laboratory became a hub of activity for AI research, and many of the ideas and concepts that would later shape the field were developed there.
The main goal of early AI research was to create machines that could mimic human intelligence and perform tasks such as problem-solving and decision-making. Researchers initially focused on developing simple programs that could play games like chess and checkers, but they quickly realized that more complex tasks would require more advanced algorithms and techniques.
The Rise of Expert Systems: 1970s-1980s
In the 1970s and 1980s, AI research began to shift away from the goal of creating intelligent machines and towards the development of specific applications that could perform specific tasks. One of the most prosperous areas of AI during this time was expert systems, which were designed to mimic the decision-making abilities of human experts in a particular field.
Expert systems were created by inputting large amounts of data and rules into a computer program, which could then be used to make decisions or provide recommendations based on that information. These systems were successful in several fields, including medicine, finance, and manufacturing, and they helped demonstrate AI’s practical value.
However, the success of expert systems was also limited by their reliance on a large amount of explicit knowledge being inputted into the system. If the system did not have the necessary data or rules, it could not make decisions or provide recommendations. This led to a shift in focus towards more flexible and adaptable AI systems that could learn and improve over time.
The Era of Machine Learning: 1990s-2000s
In the 1990s and 2000s, there was a resurgence of interest in AI, driven in large part by advances in machine learning. Machine learning is a subset of AI that involves the use of algorithms to automatically improve the performance of a system based on data.
One of the critical developments in machine learning was the advent of neural networks, which are modeled after the structure of the human brain and are capable of learning and adapting based on data inputs. This technology has been used to create systems that can recognize patterns and make decisions based on that information, leading to significant advances in fields such as image and speech recognition.
Other notable developments in machine learning during this time included the rise of support vector machines (SVMs) and decision trees, which are algorithms that can be used to classify and predict outcomes based on data inputs. These and other machine learning techniques have been applied to many applications, including natural language processing, financial forecasting, and even the discovery of new drugs.
Another significant development during this time was the rise of “big data,” or huge datasets that could be analyzed to extract valuable insights and patterns. Machine learning algorithms were particularly well-suited to working with big data, and the availability of large datasets helped to drive progress in the field.
Current Trends and Future Directions
Today, AI is being used in a wide range of applications, from self-driving cars and personal assistants to medical diagnosis and financial forecasting. Some of the current trends and developments in the field include:
- Deep learning: subfield of machine learning that uses multiple layers of artificial “neurons” to learn and analyze data. Deep learning has been successful in a number of applications, including image and speech recognition, and it has the potential to revolutionize a wide range of industries.
- Natural language processing: This is the ability of a machine to understand and generate human-like language, which has applications in areas such as language translation and voice recognition. Recent advances in natural language processing have made it possible for machines to understand and respond to complex and nuanced human language, and it is expected that this technology will continue to improve in the future.
- Robotics: AI is being used to create robots that can perform a wide range of tasks, from manufacturing and assembly to search and rescue operations. The development of autonomous robots that can adapt to changing environments and make decisions based on data inputs is a major focus of current research, and it is expected that this technology will have significant impacts in a variety of fields.
- Ethical and societal implications: As AI becomes increasingly integrated into our lives, there are also important questions being raised about the ethical and societal implications of this technology.
Looking to the future, it is clear that AI will continue to play a major role in our lives and the way we live and work. Some potential future developments in the field include:
- Autonomous vehicles: Self-driving cars and other vehicles that use AI to navigate and make decisions without human intervention.
- Personal assistants: AI-powered assistants that can help with tasks such as scheduling, email management, and online shopping.
- Medical diagnosis: The use of AI to analyze medical images and data to assist with diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Financial forecasting: The use of AI to analyze financial data and make predictions about market trends and investment opportunities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the history of AI is a fascinating and complex one, marked by significant advances and setbacks. From its earliest roots in the 1950s to the present day, AI has come a long way, and it is now being used in a wide range of applications that are changing the way we live and work. As the field continues to evolve, it will be interesting to see how AI will shape the future and what new developments and applications will emerge.