Mohamed Mohana
PMI-CPMAI™ Certified | Head of AI | Digital Transformation Expert | Certified AI Scientist (CAIS™)
King Khalid University
Biography
I am a PMI Certified Professional in Managing AI (PMI-CPMAI™) and Certified AI Scientist (CAIS™) with over 5 years of experience in AI strategy, project management, and technical development. Currently serving as Head of AI Unit at King Khalid University and contributing to the Institutional Innovation Axis within the Tenth Section: Research and Innovation of the Government Digital Transformation Index, I specialize in managing AI initiatives, Large Language Models (LLMs), Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), Computer Vision, and Digital Transformation. My expertise spans from AI governance and strategy to hands-on development and deployment of enterprise AI solutions.
With deep expertise in modern AI technologies, I work extensively with LLMs, RAG systems, vector databases (like Pinecone, Weaviate, and Chroma), and vLLM for high-performance model serving. My research focuses on developing intelligent systems that combine the power of large language models with domain-specific knowledge through advanced retrieval mechanisms and vector similarity search.
I hold a Master of Engineering degree in Control and Automation using AI from Universiti Teknologi Malaysia and a Master of AI Engineering from IBM, both with distinction. My work has been recognized with multiple awards including the Digital Innovation Award from the Ministry of Communications and Information Technology of Saudi Arabia and the Best Master Research Award from IEEE Malaysia.
Download my resumé
AI Strategy & Project Management (PMI-CPMAI™)
- AI Project Management: Strategic planning, execution, and governance of AI initiatives from concept to deployment
- Digital Transformation: Leading organizational AI transformation and change management
- AI Governance & Ethics: Establishing responsible AI frameworks and compliance strategies
- Stakeholder Management: Aligning AI initiatives with business objectives and managing cross-functional teams
- Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating risks in AI projects and deployments
Research & Development Areas
- Large Language Models (LLMs): Fine-tuning, prompt engineering, and model optimization for domain-specific applications
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): Building intelligent systems that combine LLMs with external knowledge bases
- Vector Databases: Pinecone, Weaviate, Chroma, and custom vector storage solutions for semantic search
- vLLM & Model Serving: High-performance inference and deployment of large language models
- Computer Vision: Object detection, image classification, facial recognition, and video analysis
- Machine Learning: Supervised/unsupervised learning, deep learning, and feature selection
- AI for Environment: Environmental monitoring, climate prediction, and sustainability solutions
- Renewable Energy AI: Solar power prediction, energy optimization, and smart grid systems
- Natural Language Processing: Text analysis, conversational AI, and semantic understanding
- IoT & Robotics: Autonomous systems, sensor networks, and industrial automation
Technical Expertise
- LLM Technologies: GPT, BERT, T5, LLaMA, Mistral, and custom transformer models
- RAG Frameworks: LangChain, LlamaIndex, Haystack, and custom RAG pipelines
- Vector Databases: Pinecone, Weaviate, Chroma, Qdrant, and FAISS
- Model Serving: vLLM, TensorRT, ONNX, and cloud deployment (AWS, GCP, Azure)
- Programming: Python, PyTorch, TensorFlow, FastAPI, Docker, and Kubernetes
- MLOps: MLflow, Weights & Biases, Kubeflow, and CI/CD for ML systems
Honours and Awards
- 1st Place Winner EduThon V2 - King Khalid University (2023)
- Digital Innovation Award in Digital Research - MCIT (2022)
- Top 7% on StackOverflow - Stack Overflow (2022)
- Best Computer Vision Project - Fihm.ai (2020)
- Best Research Project Awards - IEEE Malaysia Section (2019)
- Competent Communicator - Toastmaster Global (2019)
- Master Dean List Student Award - Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (2019)
- Degree Dean List Student Award - Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (2018)
- Innovate Malaysia Design Competition - ViTrox Corporation Berhad (2018)
- Best Capstone Project Lab - Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (2017)
- AI Project Management (PMI-CPMAI™)
- Digital Transformation & AI Strategy
- AI Governance & Ethics
- Large Language Models (LLMs)
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
- Vector Databases & Embeddings
- vLLM & Model Serving
- Computer Vision
- Classical Machine Learning
- AI for Environment
- AI in Renewable Energy
- NLP & Conversational AI
- Feature Selection
- MLOps & Model Deployment
Artificial Intelligence Engineer (Master Program) (4.0/4.0), 2020
IBM
MEng in Mechatronics, Robotics, and Automation Using AI (3.9/4.0), 2019
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
BE in Mechatronics, Robotics, and Automation (3.6/4.0), 2018
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
Skills
TECHNICAL SKILLS
Python
ML & DL
Statistics
Research
Computer Vision
NLP
Drones
IoT
Arduino/Raspberry Pi
Cloud Computing
SOFT SKILLS
Communication
Public speaking
Creativity
Teamwork
Leadership
Time management
Experience
Responsibilities include:
- Leading AI initiatives and strategy
- Team management and project oversight
- PMP-based project execution
- Strategic planning and implementation
Responsibilities include:
- Machine Learning and Deep Learning implementations
- AI systems architecture and development
- Technical leadership and mentoring
- Innovation in AI solutions
Responsibilities include:
- Leading research initiatives
- Team motivation and management
- Research strategy development
- Innovation oversight
Responsibilities include:
- Research and development in AI
- Analysis, modeling, and deployment
- System efficiency optimization
- Research publication and documentation
Featured Publications
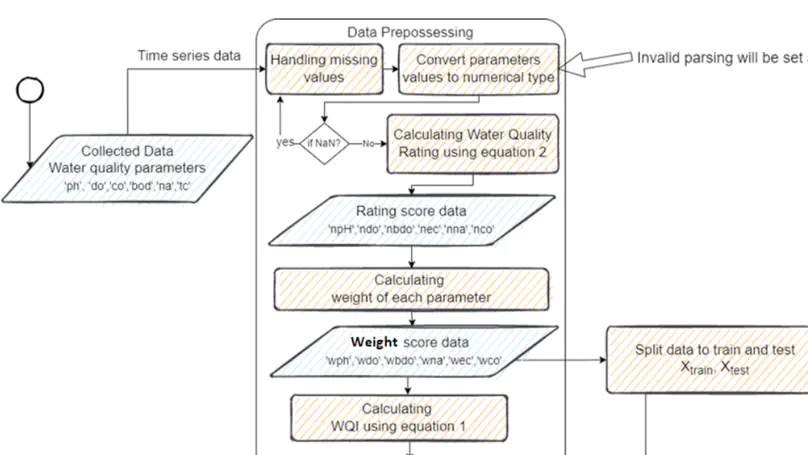
Rivers are the main sources of freshwater supply for the world population. However, many economic activities contribute to river water pollution. River water quality can be monitored using various parameters, such as the pH level, dissolved oxygen, total suspended solids, and the chemical properties. Analyzing the trend and pattern of these parameters enables the prediction of the water quality so that proactive measures can be made by relevant authorities to prevent water pollution and predict the effectiveness of water restoration measures. Machine learning regression algorithms can be applied for this purpose. Here, eight machine learning regression techniques, including decision tree regression, linear regression, ridge, Lasso, support vector regression, random forest regression, extra tree regression, and the artificial neural network, are applied for the purpose of water quality index prediction. Historical data from Indian rivers are adopted for this study. The data refer to six water parameters. Twelve other features are then derived from the original six parameters. The performances of the models using different algorithms and sets of features are compared. The derived water quality rating scale features are identified to contribute toward the development of better regression models, while the linear regression and ridge offer the best performance. The best mean square error achieved is 0 and the correlation coefficient is 1.
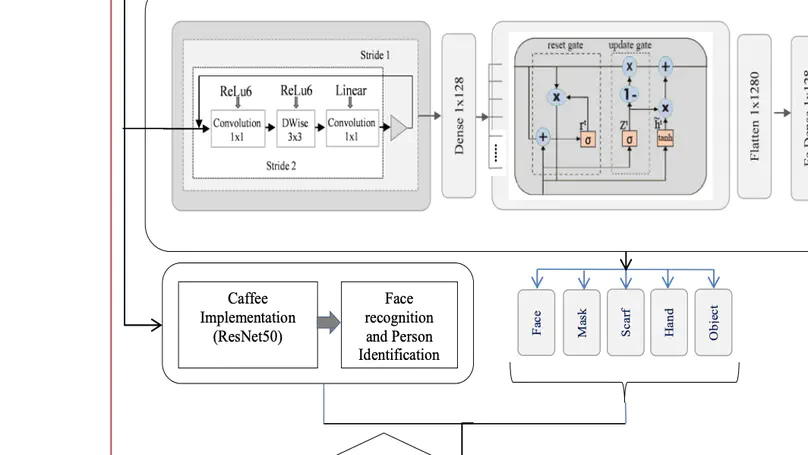
Recent period of pandemic has brought person identification even with occluded face image a great importance with increased number of mask usage. This paper aims to recognize the occlusion of one of four types in face images. Various transfer learning methods were tested, and the results show that MobileNet V2 with Gated Recurrent Unit(GRU) performs better than any other Transfer Learning methods, with a perfect accuracy of 99% in classification of images as with or without occlusion and if with occlusion, then the type of occlusion. In parallel, identifying the Region of interest from the device captured image is done. This extracted Region of interest is utilised in face identification. Such a face identification process is done using the ResNet model with its Caffe implementation. To reduce the execution time, after the face occlusion type was recognized the person was searched to confirm their face image in the registered database. The face label of the person obtained from both simultaneous processes was verified for their matching score. If the matching score was above 90, the recognized label of the person was logged into a file with their name, type of mask, date, and time of recognition. MobileNetV2 is a lightweight framework which can also be used in embedded or IoT devices to perform real time detection and identification in suspicious areas of investigations using CCTV footages. When MobileNetV2 was combined with GRU, a reliable accuracy was obtained. The data provided in the paper belong to two categories, being either collected from Google Images for occlusion classification, face recognition, and facial landmarks, or collected in fieldwork. The motive behind this research is to identify and log person details which could serve surveillance activities in society-based e-governance.
Smart home is a concept that aims to maximize the comfort of occupant while consuming energy as low as possible. The comfort and energy consumption are contradicting factors in smart homes. Enhancing comfort often requires considerable energy. On the other hand, minimizing energy may result in less comfort to the residence. Thus, maximizing comfort while minimizing energy consumption is a challenging process. In this paper, bat algorithm (BA) based solution is proposed to tackle this problem. Three main parameters that influence the occupant’s comfort, namely, temperature, illumination, and indoor air quality, are considered. The algorithm optimizes towards the best set of values for the three parameters. In this work, exponentially increasing inertia weight is introduced to BA for performance improvement. A secondary dataset consisting of 48 environmental values is optimized using the proposed algorithm. The performance of BA with exponential inertia weight is proven as significantly better than the original BA and other variants of inertia weight; random, linearly decreasing, and nonlinearly decreasing. Moreover, the comfort level achieved by BA with exponential inertia weight is found to be better than previously reported works using firefly algorithm, genetic algorithm, ant colony optimization, and artificial bee colony algorithm. The superior performance is achieved due to better convergence behaviour. Summarily, applying BA with exponential inertia weight is a novel contribution that is essential for providing smart home system a solution that ensures optimum comfort at minimal energy consumption.
Recent Publications
Recent Posts
Recent & Upcoming Talks
Contact
PMI-CPMAI™ Certified | AI Project Management & Consulting | Digital Transformation Expert
- mmuhanna@kku.edu.sa
- Center for Artificial Intelligence (CAI), King Khalid University, Abha 61421, Saudi Arabia